Experience sharing of testing institutions: detection and identification of resistance of common electronic components
Date:2021-04-29 14:23:00 Views:3256
As a worker in the electronics industry, resistance is well known. There is no doubt about its importance. It is said that "resistance is the most used component in all electronic circuits." Resistance, because the substance hinders the current, it is called the resistive substance under this action. Resistance will lead to the change of electron flow. The smaller the resistance, the greater the electron flow, and vice versa. A substance with no or little resistance is called an electrical conductor, or conductor for short. Materials that cannot form current transmission are called electrical insulators, or insulators for short. In physics, resistance is used to represent the resistance of a conductor to current. The greater the resistance of the conductor, the greater the resistance of the conductor to the current. The resistance of different conductors is generally different. Resistance is a characteristic of the conductor itself. Resistance element is an energy dissipation element that hinders the current. The resistance value of the resistance element is generally related to the temperature. The physical quantity that measures the resistance affected by the temperature is the temperature coefficient, which is defined as the percentage of the change in the resistance value when the temperature increases by 1 ℃. The resistance is represented by "R" plus a number in the circuit. For example, R1 represents the resistance numbered 1. The main functions of resistance in the circuit are shunting, current limiting, voltage dividing, bias, etc.
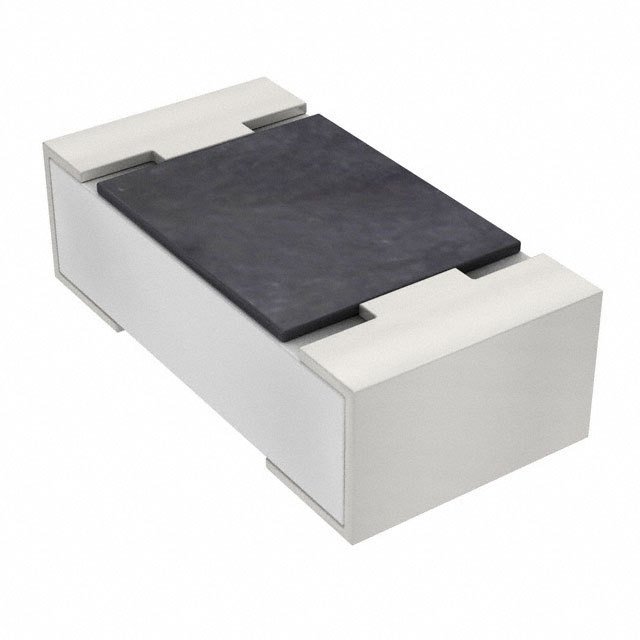

Identification of resistors
Resistors have no polarity (positive and negative). The basic feature of resistive elements is to consume energy or absorb energy. The symbol of resistance in the circuit is(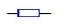 )Or(
)Or(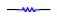 )The letter symbol is r, the unit is Ohm (Ω), and there are kiloohm (K Ω), megaohm (m Ω), 1 megaohm (m Ω) = 1000 kiloohm (K Ω) = 106 Ω. The volume of the resistor is very small. Generally, the resistance value, accuracy, material, power and other items are marked on the surface of the resistor. The commonly used resistor in the workshop is chip ceramic resistor (also known as patch resistor), and its resistance value is marked on the resistance surface. There are two methods for marking resistance parameters: text direct marking and color ring marking. Read the resistance of patch, for example: 103 = 10x103 = 10K Ω, 333 = 33x103 = 33K Ω, 472 = 47x102 = 4.7K Ω, etc. The method of reading is that the first two digits are significant numbers, the third digit is the power of ten, or the number is a few zeros added to the last side.
)The letter symbol is r, the unit is Ohm (Ω), and there are kiloohm (K Ω), megaohm (m Ω), 1 megaohm (m Ω) = 1000 kiloohm (K Ω) = 106 Ω. The volume of the resistor is very small. Generally, the resistance value, accuracy, material, power and other items are marked on the surface of the resistor. The commonly used resistor in the workshop is chip ceramic resistor (also known as patch resistor), and its resistance value is marked on the resistance surface. There are two methods for marking resistance parameters: text direct marking and color ring marking. Read the resistance of patch, for example: 103 = 10x103 = 10K Ω, 333 = 33x103 = 33K Ω, 472 = 47x102 = 4.7K Ω, etc. The method of reading is that the first two digits are significant numbers, the third digit is the power of ten, or the number is a few zeros added to the last side.
Function of resistor
The first main function of the resistor is to limit the current (or to block the current). According to Ohm's law I = u / R, when the voltage U is constant, the current I flowing through the resistance is inversely proportional to the resistance R. by selecting a resistor with appropriate resistance value, the current I can be limited to a certain value, which is the current limiting effect of the resistor. The second main function of the resistor is to reduce the voltage. When the current flows through the resistor, it will produce a voltage drop on the resistor. The voltage drop is directly proportional to the product of resistance value R and current, that is, u = IR Using the step-down effect of the resistor, the higher power supply voltage can meet the requirements of the circuit working voltage. The third function is the function of partial pressure and shunt.
_20210429142235_310.jpg)
Testing methods and experience sharing of basic resistors:
1. Detection of fixed resistors.
A. Connect the two probes (regardless of positive and negative) with the pins at both ends of the resistance to measure the actual resistance value. In order to improve the measurement accuracy, the measuring range should be selected according to the nominal value of the measured resistance. Due to the nonlinear relationship of Ohm scale, the division of the middle section is relatively fine. Therefore, the pointer indication value should fall to the middle section of the scale as far as possible, that is, within 20% ~ 80% radian range at the beginning of the full scale, so as to make the measurement more accurate. According to the resistance error level. Errors of ± 5%, ± 10% or ± 20% are allowed between the reading and the nominal resistance value respectively. If it is inconsistent and exceeds the error range, it indicates that the resistance value has changed.
B. Note: during the test, especially when measuring the resistance of more than tens of K Ω, do not touch the probe and the conductive part of the resistance; At least one end of the detected resistance shall be welded off from the circuit to prevent other components in the circuit from affecting the test and causing measurement error; Although the resistance value of the color ring resistance can be determined by the color ring mark, it is best to use a multimeter to test its actual resistance value.
2. Detection of cement resistance.
The method and precautions for testing cement resistance are exactly the same as those for testing ordinary fixed resistance.
3. Detection of fused resistors.
In the circuit, when the fusing resistor is fused and open circuit, it can be judged according to experience: if the surface of the fusing resistor is found to be blackened or charred, it can be determined that it is caused by its overload and the current passing through it exceeds many times the rated value; If there is no trace on its surface and there is an open circuit, it indicates that the current flowing is just equal to or slightly greater than its rated fusing value. For the judgment of the quality of the fused resistor without any trace on the surface, the multimeter R can be used × To ensure accurate measurement, one end of the fuse resistor shall be welded off the circuit. If the measured resistance value is infinite, it indicates that the fusing resistor has failed and open circuit. If the measured resistance value is far from the nominal value, it indicates that the resistance has changed and should not be used again. In the maintenance practice, it is found that a few fuse resistors are broken down and short circuited in the circuit, which should also be paid attention to during detection.
4. Detection of potentiometer.
When checking the potentiometer, first turn the handle to see whether the handle rotates smoothly, whether the switch is flexible, whether the "click" sound is clear when the switch is on and off, and listen to the friction sound between the internal contact point of the potentiometer and the resistor. If there is a "rustle" sound, it indicates that the quality is not good. When testing with a multimeter, first select the appropriate resistance gear of the multimeter according to the resistance value of the potentiometer to be measured, and then test according to the following methods.
A. Use the ohm block of the multimeter to measure both ends of "1" and "2", and its reading should be the nominal resistance value of the potentiometer. If the pointer of the multimeter does not move or the resistance value is much different, it indicates that the potentiometer has been damaged.
B. Check whether the movable arm of the potentiometer is in good contact with the resistor. Measure both ends of "1" and "2" (or "2" and "3") with the ohm gear of the multimeter, and rotate the rotating shaft of the potentiometer counterclockwise to close to the "off" position. At this time, the smaller the resistance value, the better. Then rotate the shaft handle slowly clockwise, the resistance value should gradually increase, and the pointer in the meter should move smoothly. When the shaft handle is rotated to the extreme position "3", the resistance value shall be close to the nominal value of the potentiometer. If the pointer of the multimeter jumps during the rotation of the shaft handle of the potentiometer, it indicates that the movable contact has the fault of poor contact.
5. Detection of positive temperature coefficient thermistor (PTC).
When testing, use multimeter R × Gear 1, which can be operated in two steps:
A. Normal temperature detection (indoor temperature close to 25 ℃); Contact the two probes with the two pins of the PTC thermistor, measure the actual resistance value, and compare it with the nominal resistance value. If the difference between the two is within ± 2 Ω, it is normal. If the difference between the actual resistance value and the nominal resistance value is too large, it indicates that its performance is poor or damaged.
B. Heating detection; On the basis that the normal temperature test is normal, the second step of test heating test can be carried out. Heat a heat source (such as electric soldering iron) close to the PTC thermistor, and monitor whether the resistance value increases with the increase of temperature with a multimeter. If so, it indicates that the thermistor is normal. If the resistance value does not change, it indicates that its performance has deteriorated and can not be used anymore. Be careful not to make the heat source close to the PTC thermistor or directly contact the thermistor to prevent it from being burned.
6. Detection of negative temperature coefficient thermistor (NTC).
(1) . measure the nominal resistance RT
The method of measuring NTC thermistor with multimeter is the same as that of ordinary fixed resistance, that is, the actual value of RT can be measured directly by selecting an appropriate resistance block according to the nominal resistance value of NTC thermistor. However, NTC thermistor is very sensitive to temperature, so the following points should be paid attention to during the test:
A. RT is measured by the manufacturer when the ambient temperature is 25 ℃, so when measuring RT with a multimeter, it should also be carried out when the ambient temperature is close to 25 ℃ to ensure the reliability of the test.
B. The measured power shall not exceed the specified value to avoid measurement error caused by current thermal effect.
C. Pay attention to correct operation. During the test, do not hold the thermistor with your hands to prevent the human body temperature from affecting the test.
(2) . estimated temperature coefficient α t
First measure the resistance value RT1 at room temperature T1, then use an electric soldering iron as a heat source, close to the thermistor RT, measure the resistance value rt2, and use a thermometer to measure the average temperature T2 on the surface of the thermistor RT at this time, and then calculate.
7. Detection of varistor.
Use the R of the multimeter × 1K gear measures the forward and reverse insulation resistance between the two pins of the varistor, which is infinite. Otherwise, it indicates that the leakage current is large. If the measured resistance is very small, the varistor has been damaged and cannot be used.
8. Detection of photosensitive resistance.
A. Cover the light transmission window of the photoresist with a piece of black paper. At this time, the pointer of the multimeter basically remains motionless, and the resistance value is close to infinity. The higher the value, the better the photoresist performance. If this value is very small or close to zero, it indicates that the photoresist has been burned through and damaged and can no longer be used.
B. Aim a light source at the light transmission window of the photoresist. At this time, the pointer of the multimeter should swing greatly, and the resistance value should be significantly reduced. The more obvious this value is, the better the performance of the photoresist is. If this value is very large or even infinite, it indicates that the photoresist is internally open circuit damaged and can no longer be used.
C. Shine light on the light transmission window of the photoresist, and shake the small black paper on the upper part of the light shielding window of the photoresist to make it receive light intermittently. At this time, the multimeter pointer should swing left and right with the shaking of the black paper. If the pointer of the multimeter always stops at a certain position and does not swing with the shaking of the paper, it indicates that the photosensitive material of the photosensitive resistance has been damaged.




 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou





















