April Component Quality Exception Analysis Report
Date:2024-05-20 17:48:13 Views:2309

◆ Report Introduction ◆
In order to help more customers understand the information of abnormal materials, Chuangxin Testing has released a component abnormal quality analysis report to the public. We hope it can help you warn of risks, ensure safe shopping, and avoid purchasing unqualified components.
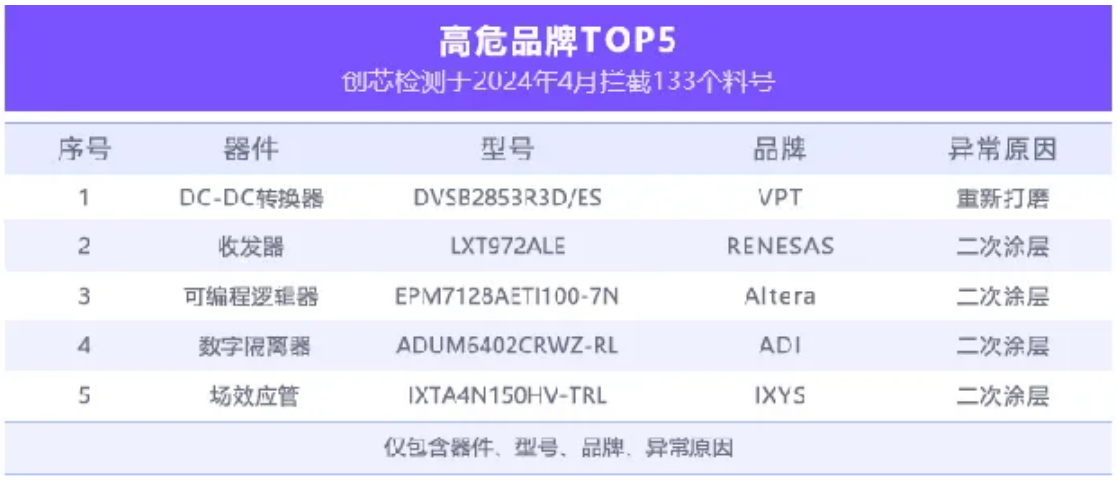
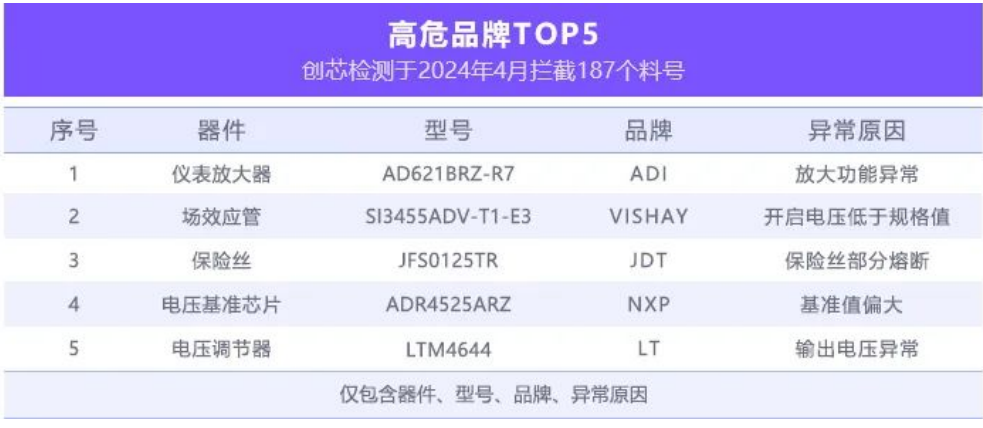
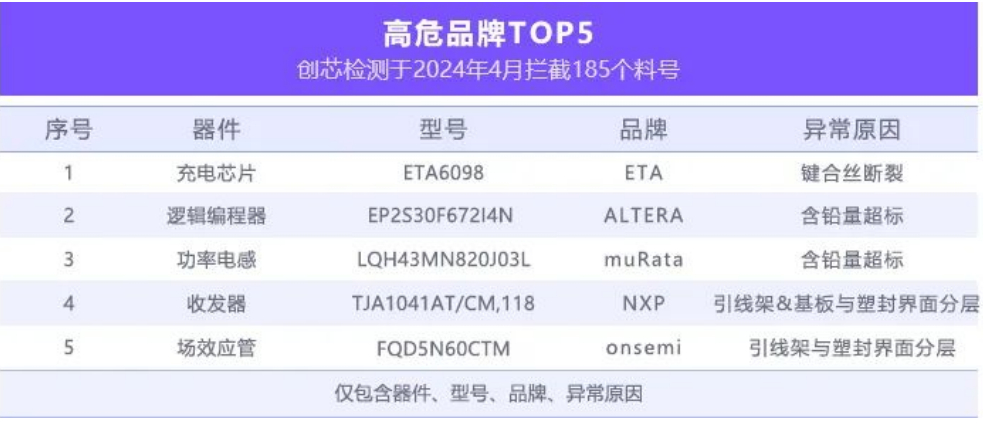
This announcement is for high-risk and high-risk materials intercepted by the laboratory in April 2024.

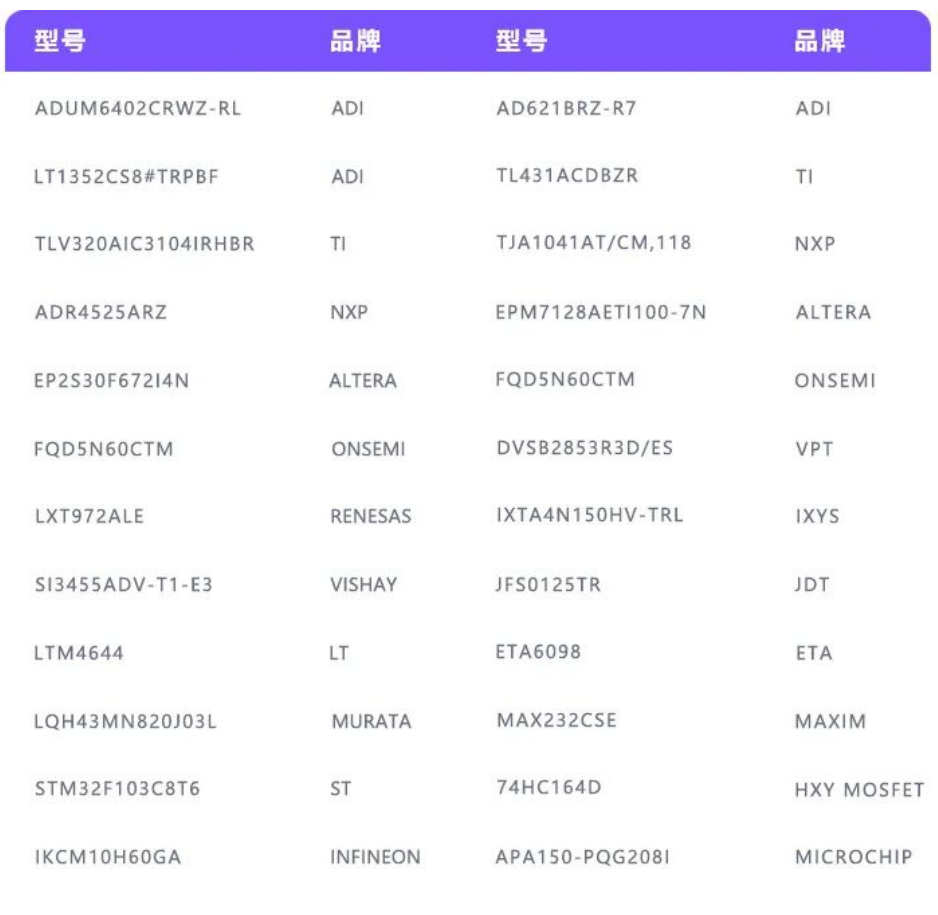
Partial models
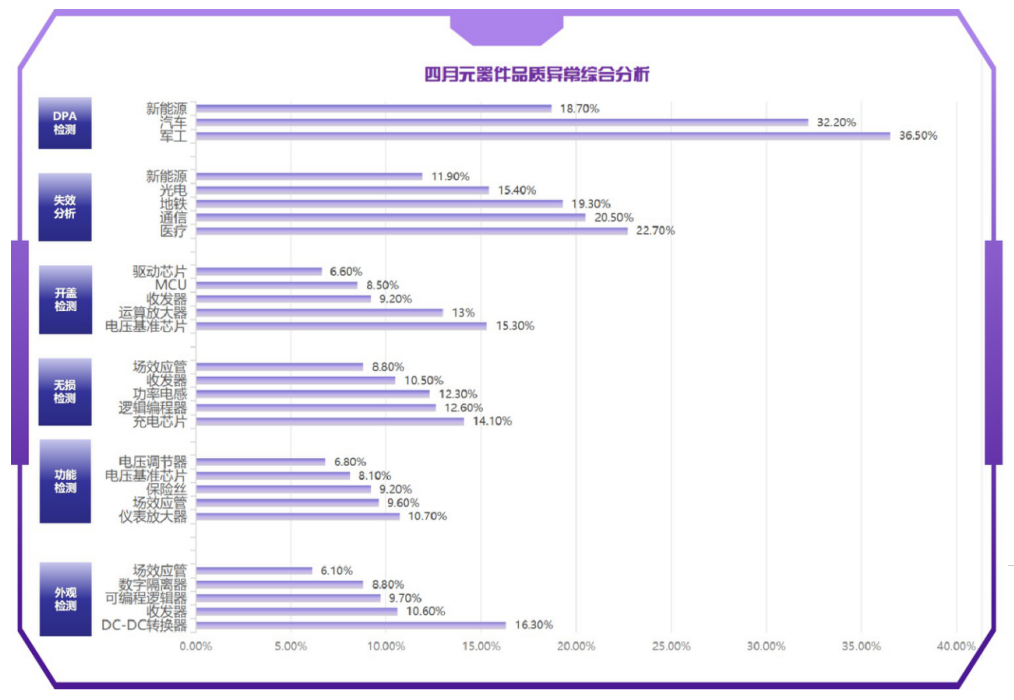
comprehensive analysis
01 Appearance inspection

Appearance inspection refers to confirming whether the received number of chips, inner packaging, humidity indicators, desiccant requirements, and outer packaging meet the requirements. The appearance inspection of a single chip mainly includes: the chip's typing, year, place of origin, whether it has been repainted, the status of the pins, whether there are re polished marks, unknown residues, and the position of the manufacturer's logo.
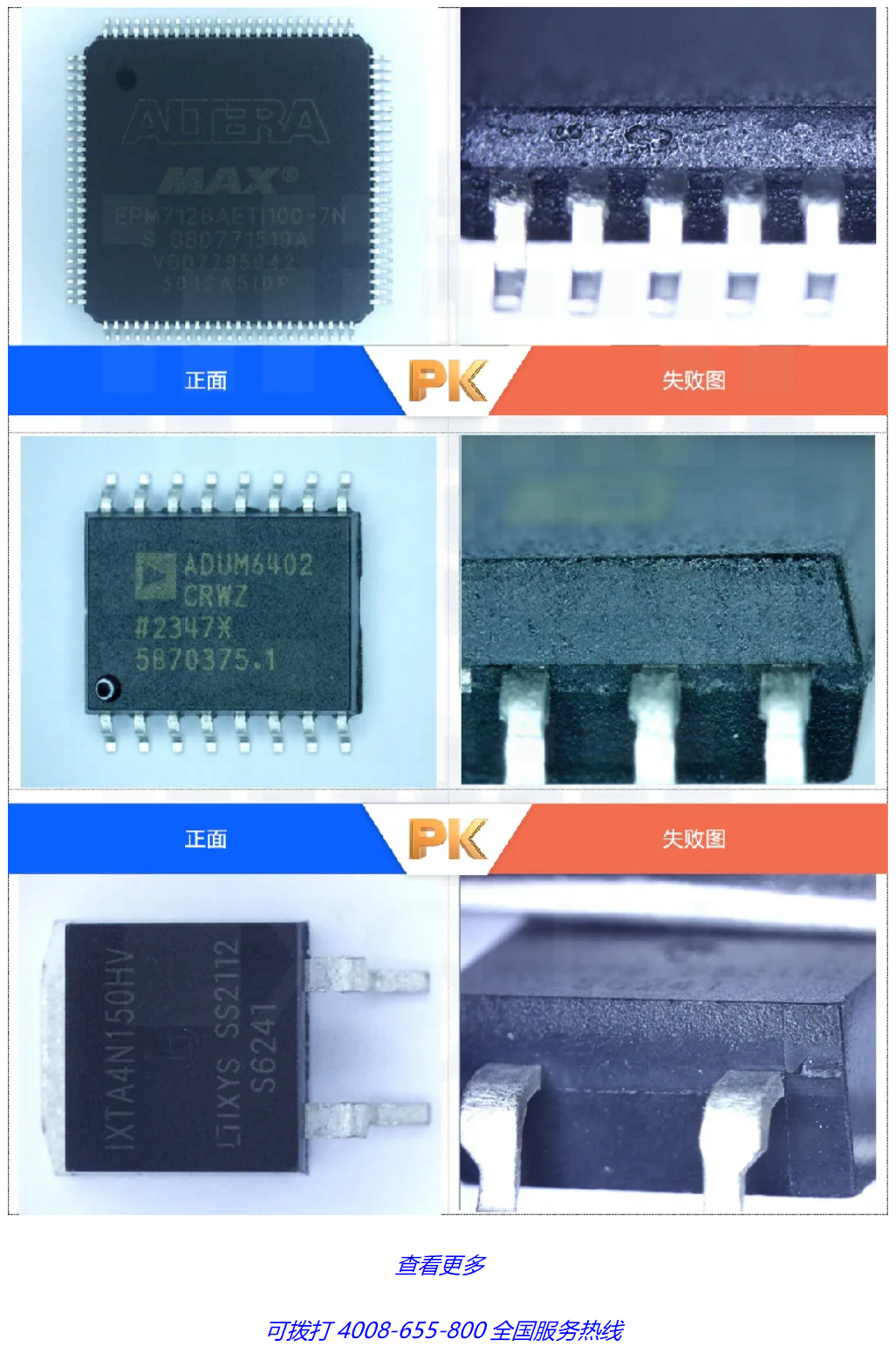
02 Function detection

Functional testing refers to conducting various necessary logic or signal status tests under specific working conditions (i.e. normal operating environment of the device, usually room temperature) and the normal working state of the device. This test is based on the original factory specifications and industry standards or specifications. Feasibility test vectors or specialized test circuits are designed to apply corresponding signal source inputs to the detection samples. Through specific conditions such as peripheral circuit adjustment control, signal amplification or conversion matching, the logical relationship of the signal and the change status of the output waveform are analyzed to detect the functional characteristics of electronic components.
There are six commonly used methods for chip functional testing, including board level testing, wafer CP testing, FT testing of packaged products, system level SLT testing, reliability testing, and multiple strategies.

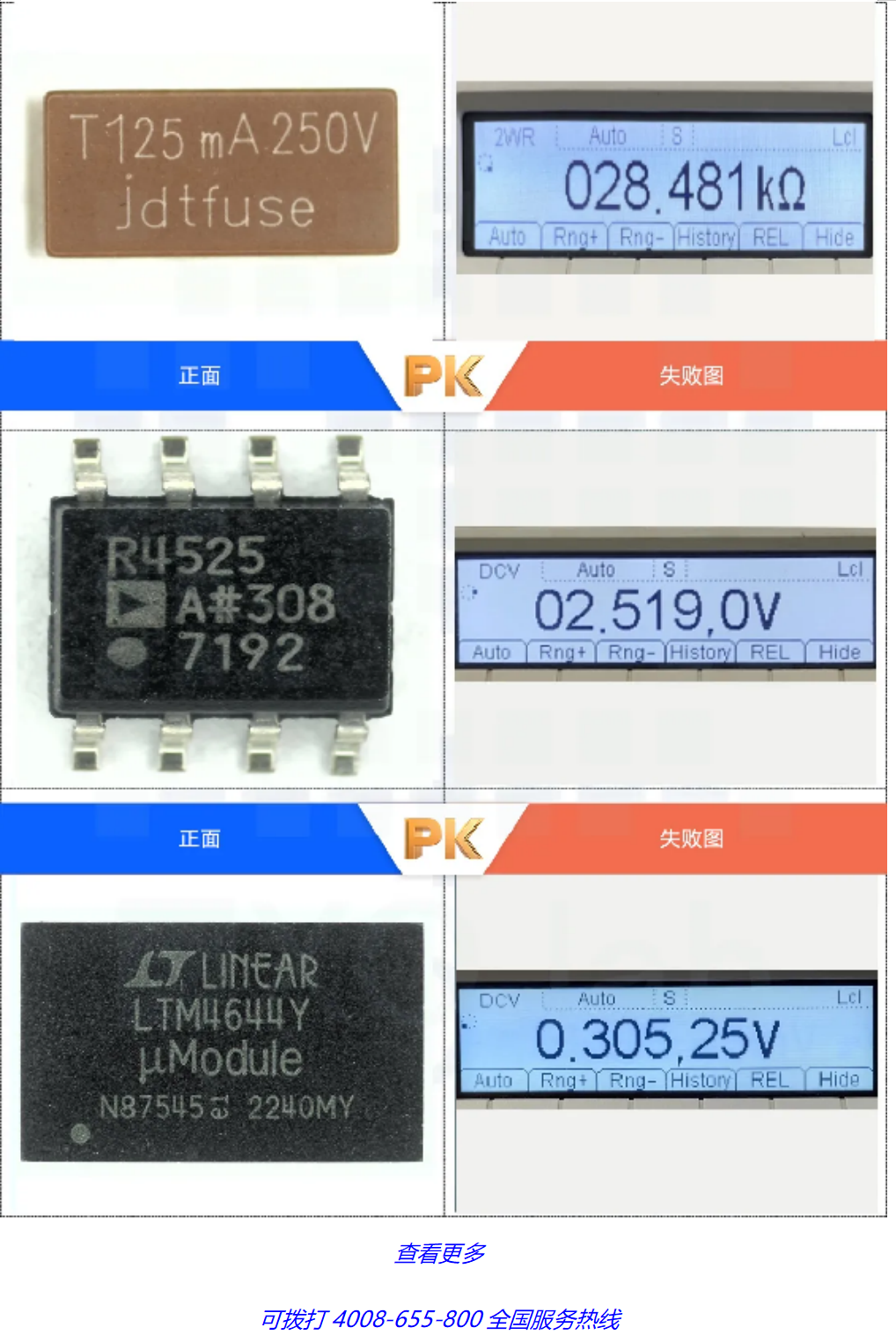
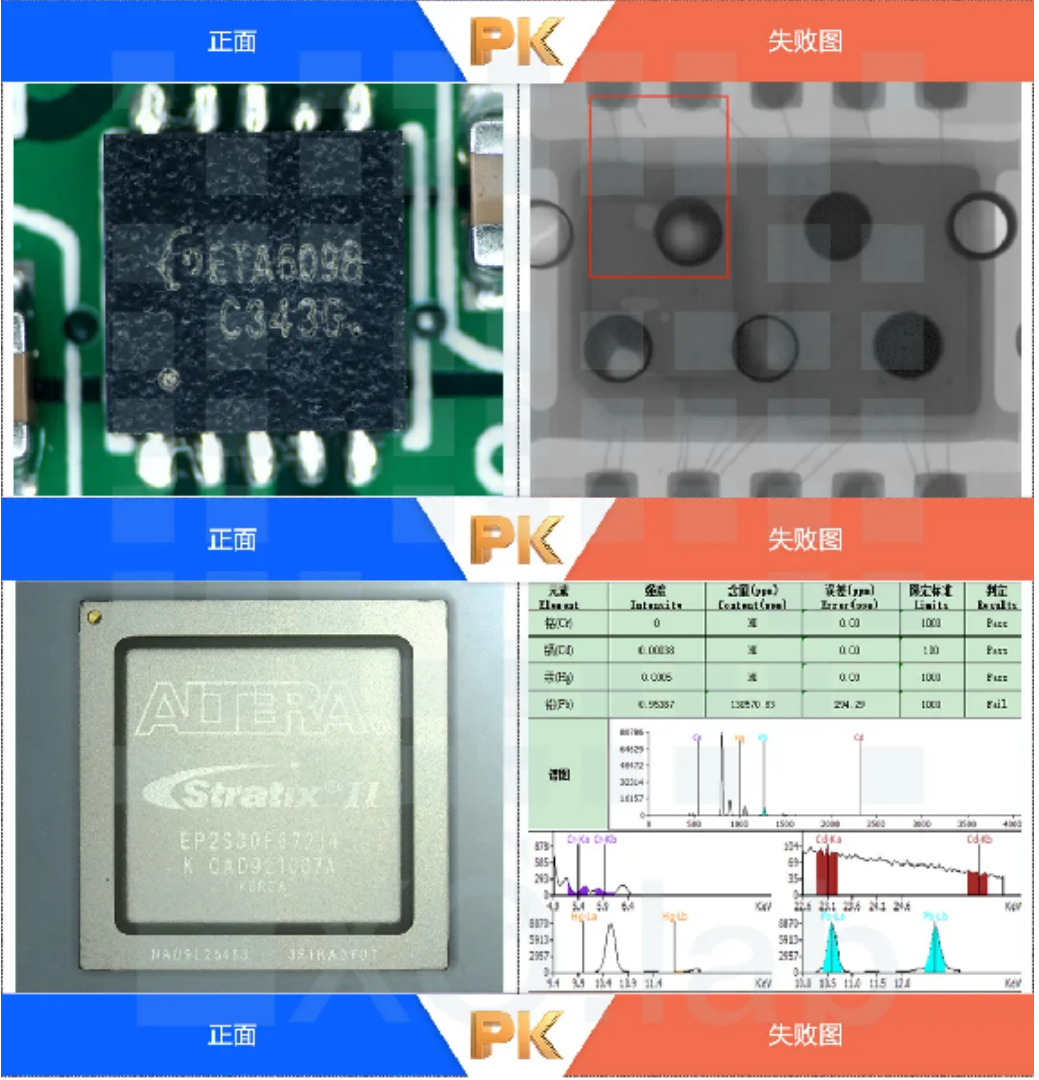
03 Non destructive testing

Non destructive testing refers to the method of inspecting and testing the structure, condition, type, quantity, shape, nature, position, size, distribution, and changes of defects inside and on the surface of an IC using physical methods and equipment, without damaging its internal organization.
The commonly used non-destructive testing methods include appearance testing, X-ray testing, thermal conductivity testing, acoustic testing, XRF testing, etc.

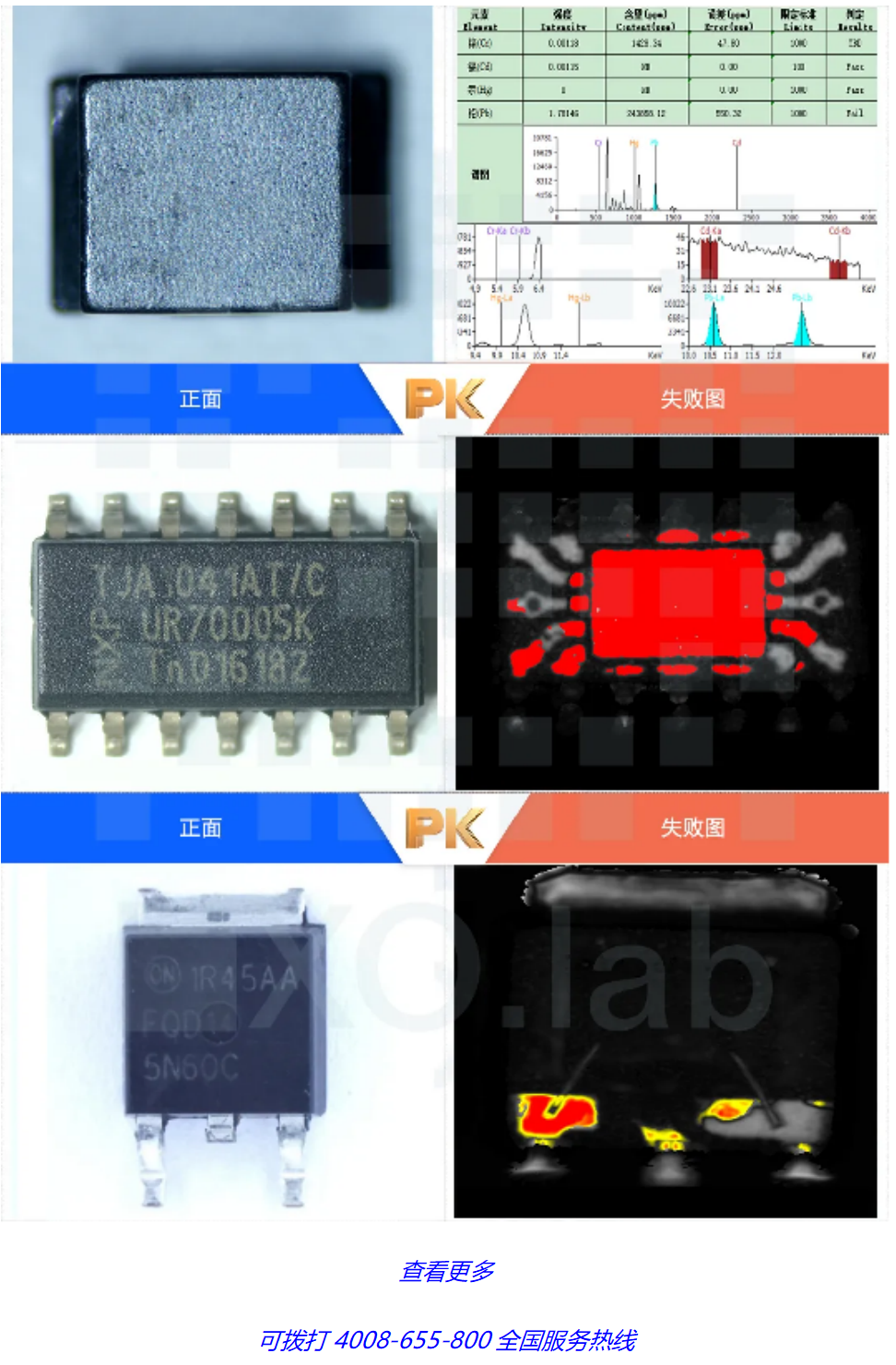
04 Cover opening inspection
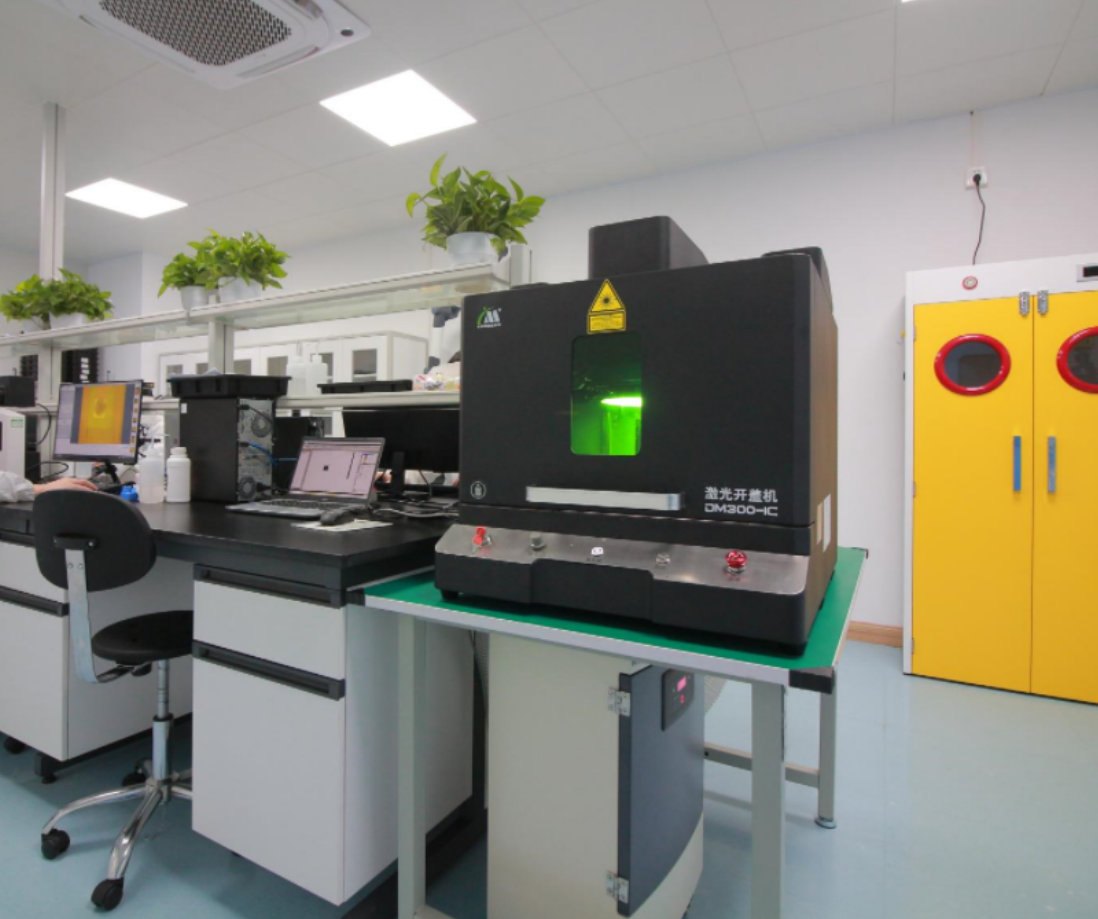

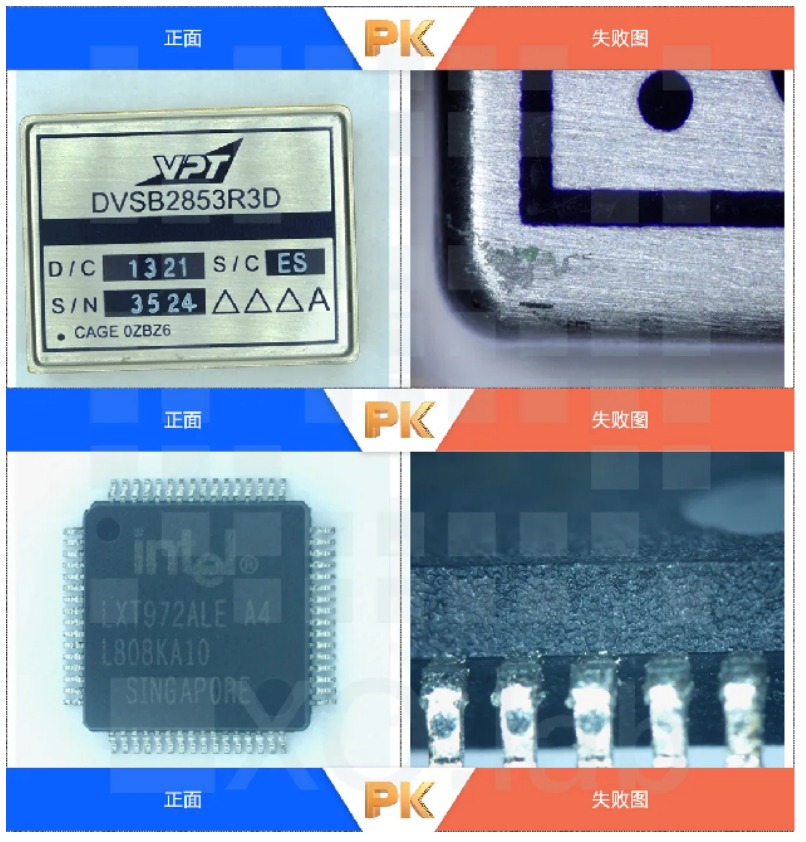
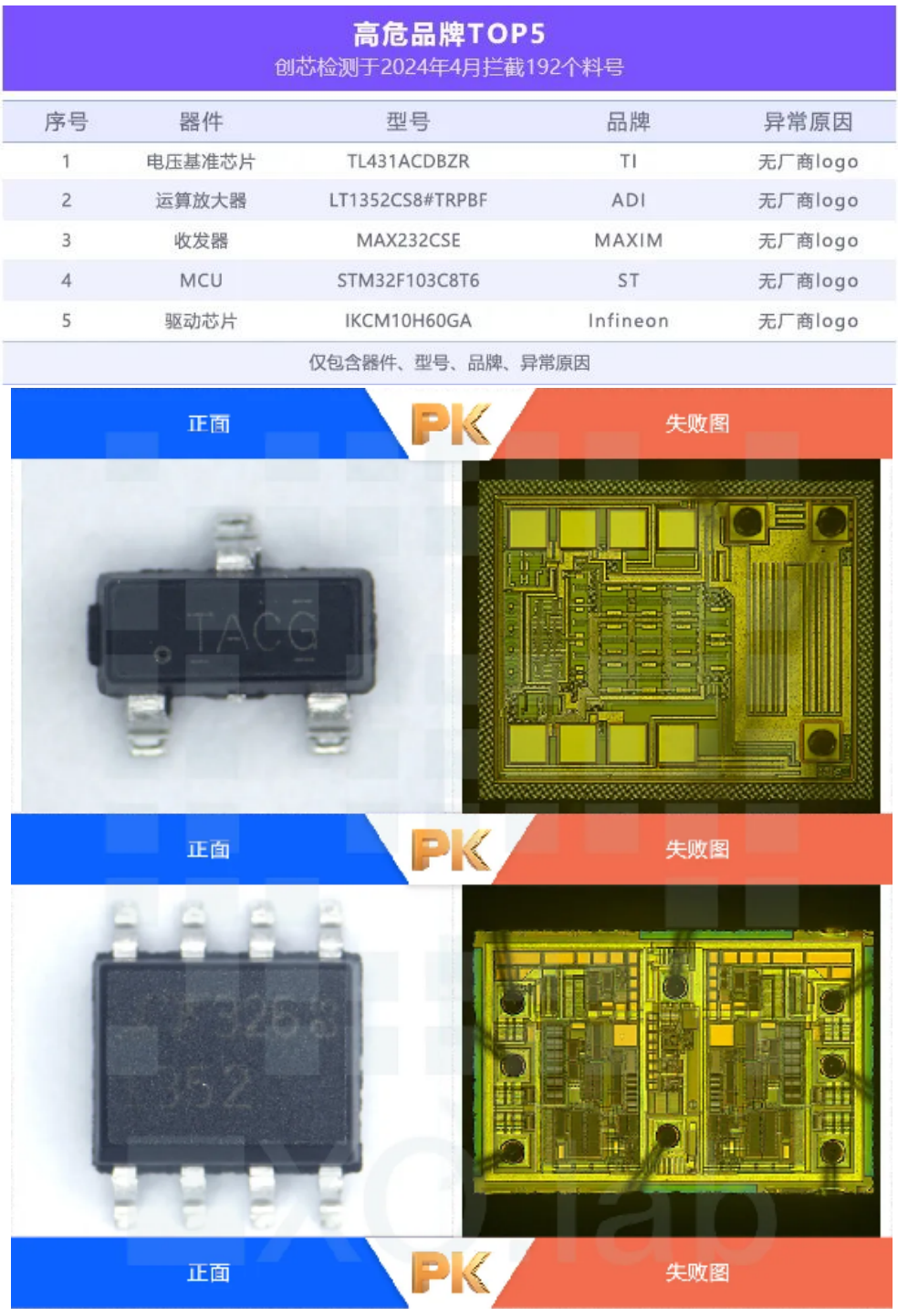
Open cover testing, also known as DECAP, is a destructive experiment that uses chemical reagents or laser etching to remove the external packaging shell of a chip, in order to check the original factory identification, layout, process defects, etc. on the surface of the internal grain. Open cover testing is a major means of authenticity detection, which can determine the authenticity and integrity of the chip.
The Decap laboratory can handle almost all IC packaging forms (COB, QFP, DIP, SOT, etc.) and wire types (AuCuAg).
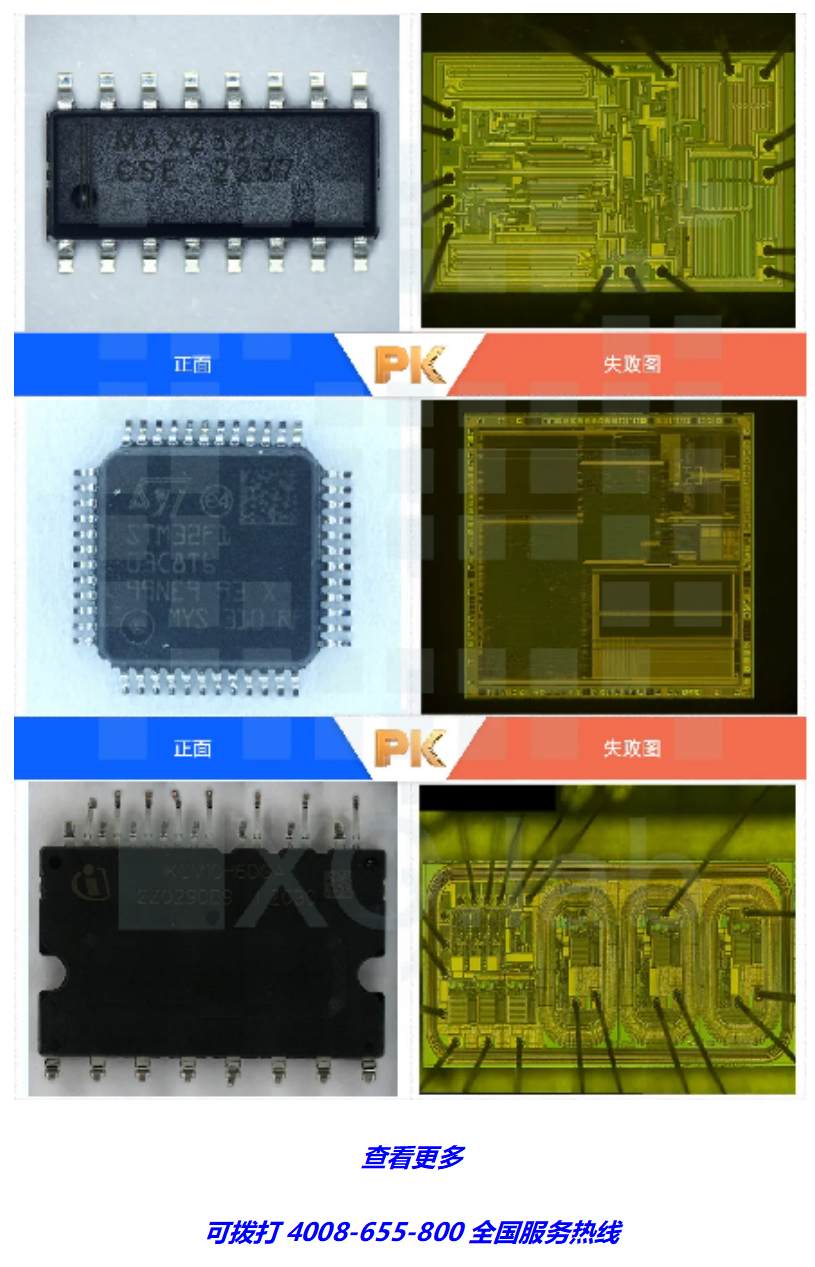
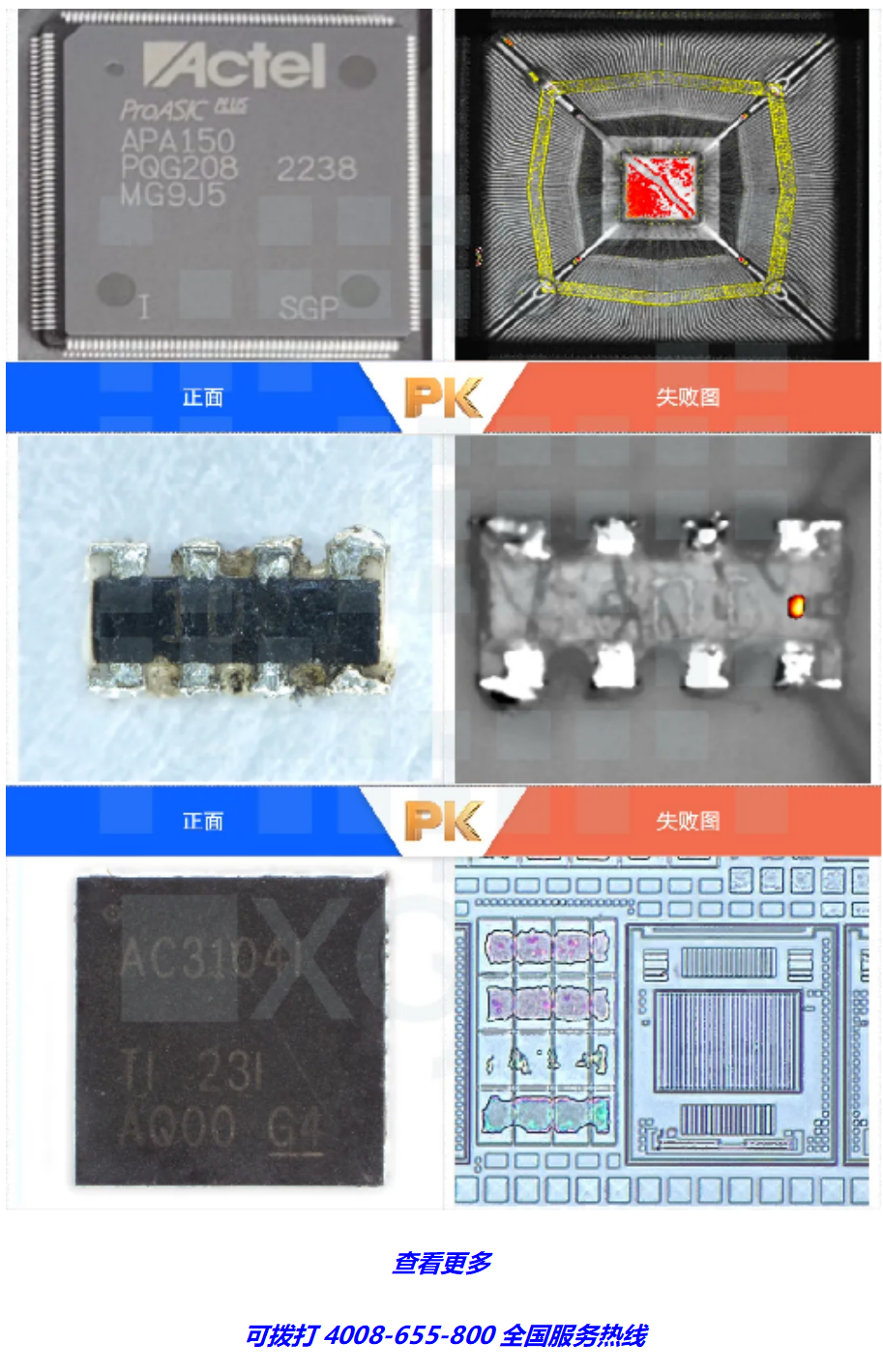
05 Failure Analysis

Through professional failure analysis equipment, various testing and analysis techniques and programs are used to confirm the failure phenomenon of electronic components, distinguish their failure modes and mechanisms, confirm the final cause of failure, and propose suggestions for improving design and manufacturing processes to prevent the recurrence of failures.
Chuangxin Testing provides components to PCBA analysis and improvement solutions. Common analysis items include: digital microscope, X-ray testing, ultrasonic scanning (SAT testing), I-V curve testing, open lid testing, FIB (focused ion beam), Thermal EMMI (InSb), gallium indium arsenide micro microscope, laser beam resistance anomaly detection, chip delamination (Delayer), cross section testing, scanning electron microscope (SEM)/EDS, etc.

06 DPA detection
Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA), abbreviated as DPA, is a series of inspections and analyses conducted on the production batch of electronic components to verify whether the design, structure, materials, and manufacturing quality of the components meet the requirements of the intended use or relevant specifications. DPA analysis is not only applicable to military electronic components, but also to civil electronic components, such as procurement inspection, incoming inspection, and quality monitoring during the production process.
No specific display for project confidentiality





 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou





















