How to do failure analysis? Six failure analysis methods Amway gives you
Date:2021-05-31 18:26:00 Views:8311
catalogue
| Significance of failure analysis | Main steps and contents | Detailed process |
| PCB / PCBA failure analysis | Failure analysis of electronic components | Failure analysis of metal materials |
| Failure analysis of polymer materials | Failure analysis of composite materials | Coating / plating failure analysis |
What is failure analysis? Failure analysis is a new developing subject, which has been popularized from military industry to ordinary enterprises in recent years. It is generally based on the failure mode and phenomenon, through analysis and verification, simulate and reproduce the failure phenomenon, find out the cause of failure, and dig out the failure mechanism. Failure analysis plays an important role in ensuring and improving the reliability and quality of products. Failure analysis needs to be introduced in product R & D, production and use. It also has strong practical significance in improving product quality, technology development and improvement, product repair and arbitration of failure accidents. So how to do failure analysis? The following failure analysis methods are given to you by Amway.
Significance of failure analysis
1. Failure analysis is a necessary means to determine the chip failure mechanism.
2. Failure analysis provides necessary information for effective fault diagnosis.
3. Failure analysis provides necessary feedback information for design engineers to continuously improve or repair the chip design and make it more consistent with the design specifications.
4. Failure analysis can evaluate the effectiveness of different test vectors, provide necessary supplements for production testing, and provide necessary information basis for verification and test process optimization.
Main steps and contents of failure analysis
Chip unsealing:
Remove the IC sealant, keep the chip function intact, and keep die, bond pads, bond wires and even lead frame from damage, so as to prepare for the next chip failure analysis experiment.
SEM / SEM / EDX composition analysis:
Including material structure analysis / defect observation, element composition, conventional micro area analysis, accurate measurement of component size, etc. Probe test: quickly and conveniently obtain the internal electrical signal of IC with microprobe.
Laser cutting:
A micro laser beam is used to cut the line or a specific area on the upper layer of the chip.
Emmi detection:
Emmi low light level microscope is a highly efficient failure analysis tool, which provides a highly sensitive and non-destructive fault location method. It can detect and locate very weak luminescence (visible light and near-infrared light), so as to capture the visible light of leakage current caused by various component defects or abnormalities.
OBIRCH application (laser beam induced impedance value change test):
OBIRCH is often used for internal high impedance and low impedance analysis and line leakage path analysis. Using OBIRCH method, defects in the circuit can be located effectively, such as holes in lines and holes under through holes. The high resistance area at the bottom of the through hole can also effectively detect short circuit or leakage, which is a powerful supplement to the luminescence microscopy technology.
LG LCD hot spot detection:
The liquid crystal is used to sense the arrangement and reorganization of molecules at the IC leakage, showing a mottled image different from other areas under the microscope, so as to find the leakage area (fault point exceeding 10mA) that puzzles the designer in the actual analysis.
Fixed / non fixed point chip grinding:
Remove the gold bump planted on the LCD driver pad and keep the pad intact for subsequent analysis or rebinding.
X-ray nondestructive testing:
Detect various defects in IC package, such as layer peeling, burst, cavity and wire integrity, possible defects in PCB process, such as poor alignment or bridging, open circuit, short circuit or abnormal connection, and tin ball integrity in package.
Sam (SAT) ultrasonic flaw detection:
It can carry out non-destructive detection on the internal structure of IC packaging, and effectively detect various damages caused by water vapor or heat energy, such as: O delamination of wafer surface, O cracks in tin ball, wafer or glue filling, O pores in packaging materials, O various holes, such as holes at wafer joint surface, tin ball, glue filling, etc.
Failure analysis process
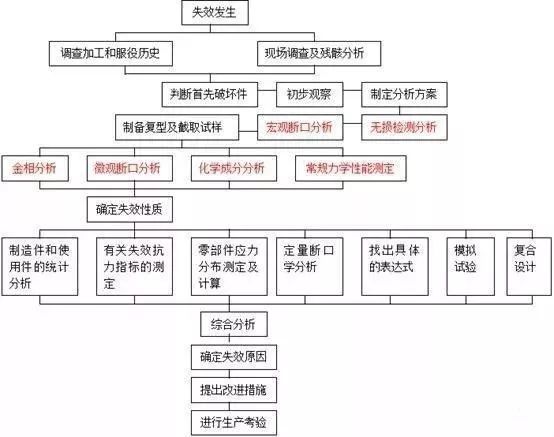
Failure analysis and detection methods of various materials
No.1
PCB / PCBA failure analysis
As the carrier of various components and the hub of circuit signal transmission, PCB has become the most important and key part of electronic information products. Its quality and reliability level determine the quality and reliability of the whole equipment.
failure mode
Plate explosion, delamination, short circuit, blistering, poor welding, corrosion migration, etc.
Common means
(1) NDT:
Appearance inspection, X-ray fluoroscopy, three-dimensional CT, C-sam, infrared thermal imaging
(2) Surface element analysis:
Scanning electron microscope and energy spectrum analysis (SEM / EDS)
Micro infrared analysis (FTIR)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS)
(3) Thermal analysis:
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Thermomechanical analysis (TMA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
Dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMA)
Thermal conductivity (steady state heat flow method, laser scattering method)
(4) Electrical performance test:
Breakdown voltage, withstand voltage, dielectric constant, electromigration
(5) Destructive performance test:
Dyeing and penetrant testing
No.2
Failure analysis of electronic components
The rapid development of electronic component technology and the improvement of reliability have laid the foundation of modern electronic equipment. The fundamental task of component reliability is to improve the reliability of components.
failure mode
Open circuit, short circuit, leakage, function failure, electrical parameter drift, unstable failure, etc
_20210531182056_315.jpg)
Common means
(1) Electrical measurement:
Connectivity test electrical parameter test function test
(2) NDT:
Unsealing Technology (mechanical unsealing, chemical unsealing, laser unsealing)
De passivation layer technology (chemical corrosion de passivation layer, plasma corrosion de passivation layer, mechanical grinding de passivation layer)
Micro area analysis technology (FIB, CP)
(3) Sample preparation technology:
Unsealing Technology (mechanical unsealing, chemical unsealing, laser unsealing)
De passivation layer technology (chemical corrosion de passivation layer, plasma corrosion de passivation layer, mechanical grinding de passivation layer)
Micro area analysis technology (FIB, CP)
(4) Micro morphology analysis:
Optical microanalysis Technology
Scanning electron microscope secondary electron image technology
(5) Surface element analysis:
Scanning electron microscope and energy spectrum analysis (SEM / EDS)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS)
(6) Nondestructive analysis technology:
X-ray fluoroscopy Technology
3D perspective technology
Reflective scanning acoustic microscopy (C-sam)
No.3
Failure analysis of metal materials
With the progress of society and the development of science and technology, metal products are more and more widely used in industry, agriculture, science and technology and people's life. Therefore, the quality of metal materials should be paid more attention.
failure mode
Improper design, material defect, casting defect, welding defect, heat treatment defect
_20210531182520_580.jpg)
Common means
(1) Microstructure analysis of metal materials:
Metallographic analysis
X-ray phase structure analysis
Surface residual stress analysis
Grain size of metal materials
(2) Composition analysis:
Direct reading spectrometer, X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS), Auger electron spectrometer (AES), etc
(3) Phase analysis:
X-ray diffractometer (XRD)
(4) Residual stress analysis:
X-ray stress tester
(5) Mechanical property analysis:
Universal testing machine, impact testing machine, hardness testing machine, etc
No.4
Failure analysis of polymer materials
The general development trend of polymer material technology is high performance, high function, compound, intelligent and green. Because of the new requirements of technology and the high requirements of products, it is necessary to find out the root cause and mechanism of failure by means of failure analysis, so as to improve product quality, process improvement and responsibility arbitration.
failure mode
Fracture, cracking, delamination, corrosion, blistering, coating falling off, discoloration, wear failure
_20210531182540_314.jpg)
Common means
(1) Composition analysis:
Fourier infrared spectrometer (FTIR)
Micro confocal Raman spectrometer (Raman)
Scanning electron microscope and energy spectrum analysis (SEM / EDS)
X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF)
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)
Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (PGC-MS)
Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis (NMR)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray diffractometer (XRD)
Time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS)
(2) Thermal analysis:
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Thermomechanical analysis (TMA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
Dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMA)
Thermal conductivity (steady state heat flow method, laser scattering method)
(3) Pyrolysis analysis:
Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC)
Melt index test (MFR)
(4) Fracture analysis:
Scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray energy spectrometer (EDS), etc
(5) Physical performance analysis:
Hardness tester, tensile testing machine, universal testing machine, etc
No.5
Failure analysis of composite materials
Composite materials are composed of two or more materials with different properties. It has the advantages of high specific strength, excellent toughness and good environmental resistance, so it can be widely used in practical production.
failure mode
Fracture, discoloration, failure, corrosion, insufficient mechanical properties, etc
Common means
(1) NDT:
Radiographic testing technology (X-ray γ X-ray, neutron ray, etc.), industrial CT, Compton Backscatter Imaging (CST) technology, ultrasonic testing technology (penetration method, pulse reflection method, tandem method), infrared thermal wave testing technology, acoustic emission testing technology, eddy current testing technology, microwave testing technology, laser holographic testing method, etc.
(2) Composition analysis:
For X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis (XRF), see component analysis in failure analysis of polymer materials.
(3) Thermal analysis:
Gravimetric analysis (TG), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), static thermomechanical analysis (TMA), dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMTA), dynamic dielectric analysis (deta)
(4) Destructive test:
Slice analysis (metallographic slice, focused ion beam (FIB) sample preparation, ion grinding (CP) sample preparation)
No.6
Coating / plating failure analysis
failure mode
Delamination, cracking, corrosion, blistering, coating / coating falling off, discoloration, failure, etc
Common means
(1) Composition analysis:
See polymer failure analysis
(2) Thermal analysis:
See polymer failure analysis
(3) Fracture analysis:
Stereomicroscope (OM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
(4) Physical properties:
Tensile strength, bending strength, etc
(5) Simulation test (if necessary)
The test shall be carried out under the same working conditions or under simulated working conditions.
Submission of analysis results
1) Propose the nature and cause of failure
2) Propose preventive measures (suggestions)
3) Submit failure analysis report
Significance of failure analysis:
Product quality is the lifeline of an enterprise. Improving product quality and prolonging the service life of parts are the foundation of enterprises.
Significance of part failure analysis:
1. Reduce and prevent the repeated failure of similar mechanical parts, ensure product quality and improve product competitiveness.
2. Analyze the failure causes of mechanical parts to provide scientific basis for accident liability identification, detection of criminal cases, determination of compensation liability, insurance business, modification of product quality standards, etc.
3. Provide information for enterprise technology development and transformation, increase the technical content of enterprise products, and obtain greater economic benefits.




 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou





















