What are the common detection methods for failure analysis? Basic cause analysis of component failure
Date:2021-09-24 12:00:56 Views:3309
Failure mechanism is a physical or chemical process that leads to the failure of parts, components and materials. The inducing factors of this process are internal and external. When studying the failure mechanism, we usually start with the external inducing factors and failure manifestations, and then study the more hidden internal factors. This is also the reverse thinking and exploration for people to understand the essence and development law of things, the basic link and key to change failure into safety, and the source and way for people to deepen their understanding of objective things. In order to help you have an in-depth understanding, this paper will summarize the component failure analysis and detection methods. If you are interested in what this article will cover, read on.
Failure analysis classification
1. Classification by function
According to the definition of failure, the criterion of failure is whether the specified function is lost. Therefore, the classification of failures can be classified by function. For example, according to the specified functions of different materials, the types of material failure can be divided by various material defects (including composition, performance, organization, surface integrity, variety, specification, etc.).
2. Classification according to material damage mechanism
According to the physical and chemical essential mechanisms and process characteristics of material changes during mechanical failure,
3. Classification according to the time characteristics of mechanical failure
(1) Early failure can be divided into accidental early failure and depletion period failure.
(2) Sudden failure can be divided into progressive (gradual) failure and intermittent failure.
4. Classification by consequences of mechanical failure
(1) Partial failure
(2) Complete failure
(3) Mild failure
(4) Hazardous (severe) failure
(5) Catastrophic (fatal) failure
The classification of failure analysis can generally be divided into:
(1) Narrow failure analysis: the main purpose is to find out the direct cause of product failure.
(2) Generalized failure analysis: not only to find out the direct cause of product failure, but also to find out the weak links in technical management.
(3) Failure analysis in new product development stage: failure analysis of failed research products.
(4) Failure analysis in product trial stage: failure analysis is performed on the failed trial products.
(5) Failure analysis at the service stage of finalized products: failure analysis shall be carried out for the invalid finalized products.
(6) Failure analysis of repaired products in service stage: failure analysis of failed repaired products.
Failure analysis and common detection methods
1. Non destructive testing (NDT) is also called non-destructive testing
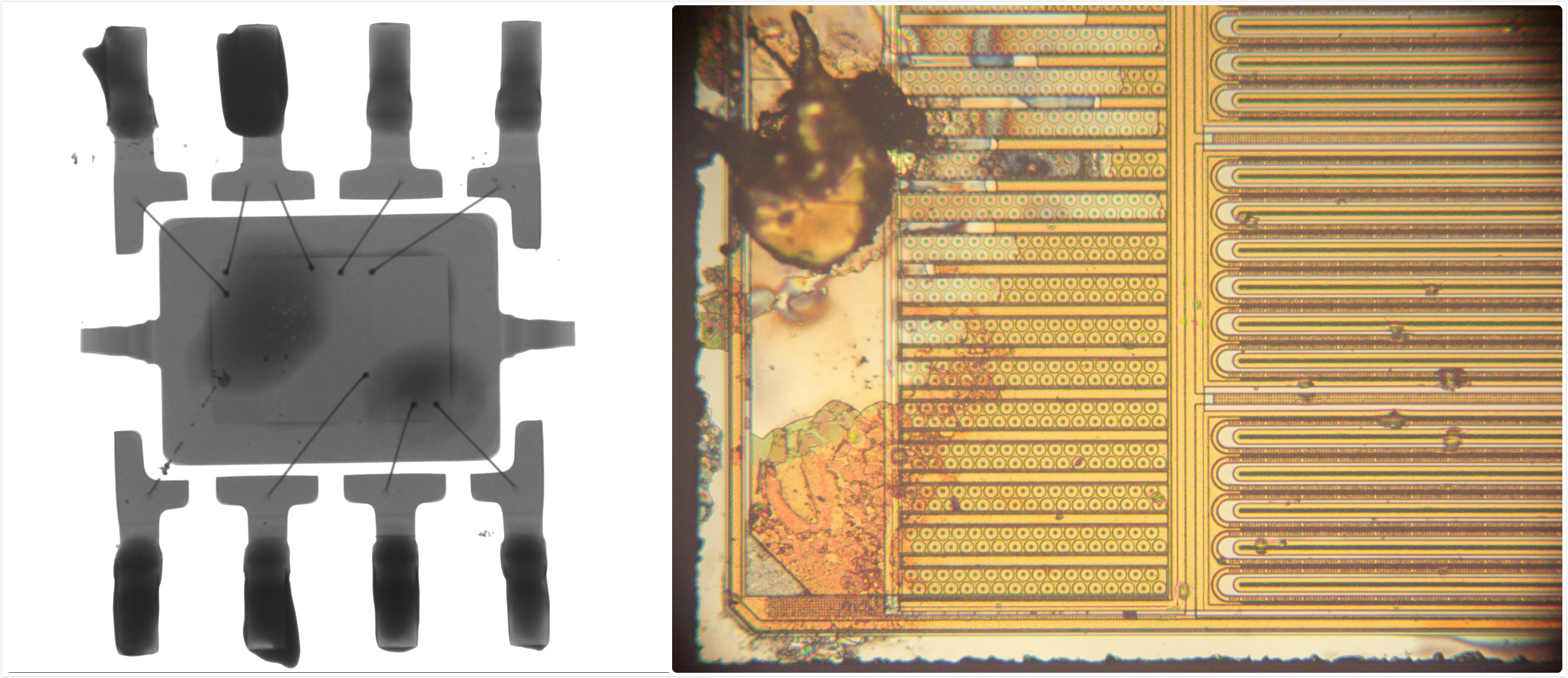
It refers to the change of thermal, acoustic, optical, electrical, magnetic and other reactions caused by abnormal internal structure or defects of materials, using physical or chemical methods and modern technology, equipment and equipment, on the premise of not damaging or affecting the service performance of the tested object and not damaging the internal organization of the tested object Inspection and test methods for the type, nature, quantity, shape, position, size, distribution and changes of status and defects.
Nondestructive testing methods: eddy current testing (ECT), radiographic testing (RT), ultrasonic testing (UT), magnetic particle testing (MT) and liquid penetrant testing (PT). Other nondestructive testing methods: acoustic emission testing (AE), thermal imaging / infrared (TIR), leakage test (LT), AC field measurement technology (acfmt), magnetic flux leakage testing (MFL), far-field test and detection method (RFT), ultrasonic diffraction time difference method (TOFD), etc.
2. Physical testAnalyze and inspect the material to determine whether the strength bearing capacity of the material meets the standard. A test to test the ability of a material or structure to withstand stress without failure. The material strength test measures the yield limit, strength limit or fatigue limit of the material. The structural strength test determines the ultimate bearing capacity of the structure, which is not only related to the material strength, but also related to the geometry of the structure, mechanism accessories and external force action form. According to the test loading mode, it is static strength test, dynamic strength test and fatigue strength test. It can be divided into normal temperature strength test, hot (high temperature) strength test or cold (low temperature) strength test according to ambient temperature. The test equipment includes static strength test equipment, dynamic strength test equipment and fatigue strength test equipment.
3. Chemical analysis
Analysis based on the chemical reaction of substances is called chemical analysis. Chemical analysis, also known as classical analysis, has a long history and is the basis of analytical chemistry. Chemical analysis is quantitative. The amount of components to be measured is calculated according to the amount of samples, reaction products or reagents consumed and the stoichiometric relationship of the reaction. Another important analytical method, instrumental analysis, is relatively quantitative and estimated according to the standard working curve.
_20210924120024_904.jpg)
Analyze the basic causes of failure
1. Failure and failure analysis
The loss of the specified function of the product is called failure. The technical and management activities of judging the failure mode, finding out the failure cause and mechanism, and putting forward countermeasures to prevent re failure are called failure analysis.
2. Failures and accidents
Failure and accident are two closely related categories. Accidents emphasize the consequences, that is, the losses and hazards caused, while failure emphasizes the functional state of mechanical products themselves. Failure and accident often have a certain causal relationship, but there is no inevitable relationship between them.
3. Failure and reliability
Failure is the opposite of reliability. Reliability R (T) of electromechanical products refers to the ratio of products that can still meet the specified functions within time t, i.e. n (T) / N (0). N (T) is the number of products that meet the specified functions within time t, and n (0) is the total number of product tests. Cumulative failure probability f (T) is the unreliability in time t, that is, f (T) = 1-r (T) = [n (0) - n (T)] / N (0).
4. Invalid parts and waste products
Invalid parts refer to the parts that fail after entering the commodity circulation field, while scrap refers to the parts with quality problems before entering the commodity circulation field. The method used for waste analysis is often consistent with the failure analysis method.
Failure Science
It is an interdisciplinary branch that studies the theories, technologies and methods of failure diagnosis, prediction and prevention of mechanical and electrical products. The boundary between failure science and related disciplines is not clear enough. It is a developing emerging discipline.
The above is the relevant content of "failure analysis and detection methods and basic causes" brought by the core detection. Through this article, I hope it can be helpful to you. If you like this article, you might as well continue to pay attention to our website, and we will bring more wonderful content later. If you have any needs related to the inspection and testing of electronic products, please call Chuangxin testing, and we will serve you wholeheartedly.




 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou





















