What are the seven failure modes of FMEA? FMEA new seven step professional analysis
Date:2022-03-11 16:37:35 Views:7696
What is FMEA? The official definition is: FMEA, namely failure mode and effects analysis, is to analyze the subsystems, parts and processes of products and equipment one by one in the product design stage and process design stage, find out all potential failure modes and analyze their possible consequences, so as to take necessary measures in advance, A systematic activity to improve the quality and reliability of products or equipment.
In 1950, when the Grumman company of the United States developed a new jet fighter, FEMA's analytical method was used to evaluate the failure analysis of a component of the aircraft operating system; In 1957, Boeing aircraft company and Martin company officially included FMEA in the engineering instruction manual. At the same time, NASA and the military also began to apply FMEA technology; In 1993, the U.S. automotive industry integrated FMEA applications of various automotive companies in order to continuously design, develop and manufacture procedures. At that time, the three major automotive companies entrusted ASoC to integrate the potential failure mode and effect analysis reference manual sea-j-1739. China introduced FMEA technology around 1970 for aerospace and automotive industry.
_20220311163655_717.jpg)
FMEA has multiplied to the fifth generation since last century. So how much do you know about the new FMEA? Let's see
The seven step method of the new FMEA provides the structure of technical risk records in an accurate, relevant and complete manner. The new structure is as follows:
1. Accurate, because technical terms are used to describe the failure mode and its potential causes;
2. Relevant, because the failure impact describes the technical consequences of failure;
3. Complete, because it uses the method of "focus element - superior element - subordinate element", which can comprehensively review the risk.
Another significant change is to emphasize FMEA planning and preparation as the first step of FMEA. Although the definition scope has always been a part of FMEA, the new FMEA manual makes it more prominent.
For example, determine the analysis boundary (including and not including), the application of 5t (FMEA intention, time, team, task, tool), the preparation and lessons learned of FMEA database, and the clear definition of roles and responsibilities (manager, technical director, coordinator, team member), etc.
Among them, the benefits of organizing lessons learned into the FMEA database are:
1. Reduce the reoccurrence of risks caused by personnel loss and knowledge loss in the past;
2. Save time in FMEA preparation. FMEA database is a reliable starting point for FMEA of similar products and processes;
3. Make the concept of "FMEA as a dynamic document" practical;
4. Management clearly estimates and allocates resources to standardize lessons learned.
The new FMEA seven step method is more organized and plays an important role in improving the efficiency of cross functional teams:
1. It can comprehensively solve more risks;
2. The multidisciplinary review of FMEA has become eye-catching, "using technology to guide thinking" rather than "unfocused brainstorming", which avoids the depressed attitude towards FMEA.
3. Enable senior managers to understand and review the necessary actions and resources to reduce technical risks.
Comparison between old and new versions:
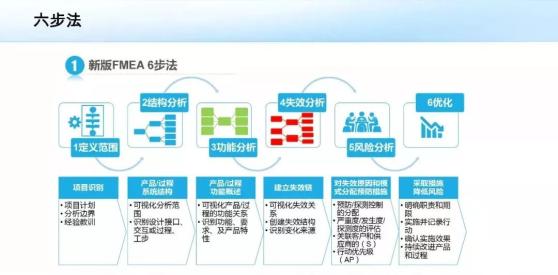

FMEA new seven step professional analysis
The first step is to define the scope
The foundation required to establish a robust FMEA is emphasized and clarified, such as:
1. The purpose, objective and limitation of FMEA and the preparation specification of technical risk documents (clear, based on reality, true and complete);
2. Put more emphasis on the commitment of senior managers to the FMEA development process;
3. Clarification related to the protection of know-how;
4. Transition strategy description of the new aiag-vda FMEA manual;
5. Use FMEA database to save organizational knowledge and lessons learned;
6. The same characteristics analyzed in DFMEA and PFMEA are used with the same failure consequences to realize the correlation between DFMEA and PFMEA.
7. Use 5T method: by clarifying the purpose and scope of the work, being consistent with the schedule of APQP stage, determining the typical roles and responsibilities of the team, the task use of seven steps, and the example of tool FMEA (including the use of software and traditional trial balance).
The second step is structural analysis
DFMEA: after understanding the system structure and decomposing the design into systems, subsystems and components, the focus elements, superior elements and subordinate elements will be described in tabular form, and additional instructions of tools used in structural analysis (such as block diagram and structure tree) will be provided.
PFMEA: its structure analysis adds more detailed manufacturing process decomposition:
1. Focusing elements of PFMEA: step station number and name of focusing process;
2. Superior element: process name (the whole manufacturing process);
3. Subordinate elements: process element 4m type (based on characteristic factor analysis), considering categories such as person / machine / material / method, so as to obtain a more complete failure cause list (FC).
The third step is functional analysis
DFMEA: more in-depth explanation of "how to correctly describe a function", including tools to support function analysis (p-diagram).
PFMEA: the description of functions and requirements related to superior and subordinate elements is added, and the description of fault impact (FE) and fault cause (FC) is clearer and complete.
The fourth step is failure analysis
DFMEA: the concepts of failure type and failure chain model are added to support more comprehensive (describing more faults) and consistent (internal consistency among Fe, FM and FC) failure description.
PFMEA:
1. Replace "failure mode (FM)" with the failure of "focus element";
2. Replace "failure effect (FE)" with the failure of "superior element" and / or "vehicle end user";
3. The failure of "process elements" replaces "failure cause (FC)".
Step 5: risk analysis
DFMEA: further distinguish between preventive control (PC) and detection control (DC). Before evaluating the incidence and detection rate, it is necessary to consider the confirmation of the effectiveness of PC and DC. After determining the severity, incidence and detection degree, DFMEA "action priority (AP)" replaces "RPN", and determines the action priority according to the high, medium and low levels of AP.
PFMEA:
1. Replace "classification column" with "special characteristics" and "filter code";
2. Replace "occurrence degree" with "occurrence degree of FC";
3. The occurrence degree is based on "predicting the occurrence of FC", so it is necessary to determine the actual effectiveness of prevention and control (PC);
4. Current process control, replace "preventive measures" with "existing preventive control (PC) of failure cause (FC)";
5. Current process control, "detection measures" will be replaced by "detection of failure cause (FC)" or "current detection control of failure mode (FM)";
6. Replace "detection measures" with "FC or FM detection measures";
7. The degree of detection is now based on three factors: the maturity of detection methods, detection opportunities and detection capabilities;
8. Replace "RPN" with "action priority (AP)" of PFMEA, and determine the action priority according to the high, medium and low levels of AP.
Step 6: optimize
DFMEA: "recommended measures" are replaced by "preventive measures" and "detection measures". Added columns: "status" (plan, decision, implementation pending, completed, abandoned) and actions taken by pointing to evidence.
PFMEA: "recommended measures" are replaced by "preventive measures" and "detection measures". Added columns: "status" (plan, decision, implementation pending, completed, abandoned) and actions taken by pointing to evidence, special characteristics and remarks.
Step 7: document the results
The result document of D / PFMEA needs to report the internal situation to the management and customers
New FMEA (aiag-vda) countermeasures.




 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou





















