SERVICE

-
IC Counterfeit Detection
- IC Counterfeit Detection-Introduce
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
-
Destructive Testing
-
Value-Added Services
-
Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA)
- Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA)-Introduce
- External Visual Inspection
- X-Ray inspection
- Functional Testing (FT)
- Particle Impact Noise Detection (PIND/PIN-D)
- Hermeticity
- Internal Water Vapor
- Scanning Acoustic Tomography (SAT Testing)
- Solderability Test
- Decapsulation/Delid Test
- Bond Strength
- Die Shear Strength
- Configuration
-
Failure analysis
- Failure analysis-Introduce
-
Non-Destructive Analysis
-
Electrical Testing
-
Fault Location
-
Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA)
-
Physical Analysis
-
Engineering Sample (ES) Packaging Service
-
Competitor Analysis
-
Development and Functional Verification
- Development and Functional Verification-Introduce
-
New Product Development Testing (FT)
-
Key Functional Testing
-
Materials Analysis
- Materials Analysis-Introduce
-
FIB Circuit Edit
-
Structural Observation
-
Compositional Analysis
- EDS Analysis
-
Reliability Testing
- Reliability Testing-Introduce
-
Reliability Verification of Automotive Integrated Circuits (ICs)
-
Environmental Testing
-
Mechanical Testing
- Pull Test
- Die Strength Test
- High Strain Rate Test - Vibration Test
- Low Strain Rate Test - Bending Test
- High Strain Rate Test - Mechanical Shock Test
- Package Assembly Integrity Test - Wire Bonding Integrity
- Package Assembly Integrity Test
- Combined Vibration/Temperature/Humidity Test
- Combined Temperature/Humidity/Vibration/Altitude Test
- Free Fall Drop Test
- Box Compressive Strength Test
-
Corrosion Testing
-
IP Waterproof/Dust Resistant Test
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)-Introduce
- Immunity to Conducted Disturbances, Induced by Radio Frequency (RF) Fields
- Conducted Immunity Test
- Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) Testing for Electromagnetic Radiation
- Electrical Fast Transient/Burst (EFT/B) Test
- Voltage Flicker/Fluctuation Test
- Voltage Dips, Short Interruptions and Voltage Variations Immunity Test
- Power Frequency Magnetic Field (PFMF) Immunity Test
- Harmonic Interference Test
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Immunity Test
- Surge/Lightning Immunity Test
- Radiated Emissions (RE) Test
- Radio Frequency (RF) Test
-
Chemical Analysis
- Chemical Analysis-Introduce
-
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
-
Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (PY-GC-MS)
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
- Flame Retardancy Test
Description:
Drop testing encompasses both Package/Parcel Drops and Product Drops. Package drop testing mainly evaluates the ability of products to withstand accidental drop impacts during transportation and storage, while product drop testing assesses their ability to withstand such impacts during normal use. Package drop testing also reflects the protective capability of the packaging when subjected to vertical drops.
The drop height, number of drops, and drop direction determine the severity of the test. Different international standards and specifications have varying drop modes and drop heights depending on the product. For handheld products (e.g., mobile phones, MP3 players), most drop heights range from 100cm to 150cm. The IEC recommends a drop height of 100cm without damage for handheld products weighing ≤2kg, while MIL suggests a drop height of 122cm. Intel recommends a drop height of 150cm for hand-held products such as mobile phones.
According to reference standards, the surface for drop testing should be rigid, smooth, and made of concrete or steel. Alternatively, other surfaces such as marble can be used if necessary.
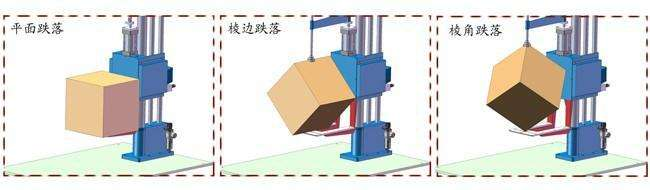
Package Drop Testing:
During drop testing, a package will be dropped in a controlled setting in different orientations—on one corner, three edges, and six faces—to measure the durability of a product.
Corner Drop: After the drop, the tested corner impacts the flat.
Edge Drop: The specimen bottom surface is inclined at a 20° angle, and then raised to the testing height before dropping, causing the edges to impact the flat.
Face Drop: The specimen is dropped in a way that its face directly impacts the flat with the surface.
Package drop testing assesses the strength of the external box or inner box and the overall stability of the product packaging in meeting quality requirements.
Product Drop Testing:

The purpose of product drop testing is to assess the product’s ability to withstand throws or accidental drops during use. The method of releasing the test sample should ensure free fall from a suspended position while minimizing interference.
ASTM standard test equipment requires a throwing ground covered with 3.0 mm (1/8in) thick rubber flooring, a minimum depth of 64 mm (2.5in) of concrete, and an area not less than 3 m2.
EN71 standard test equipment requires a throwing ground covered with 4mm thick steel plate, with a surface coating of 2mm thickness and a Shore hardness of 75±5A, placed on a non-flexible horizontal surface.
GB6675 standard test equipment requires an impact surface composed of ethylene-based polymer sheet material with a rated thickness of approximately 3mm. The ethylene-based polymer sheet should be attached to a concrete surface with a thickness of at least 64mm. The surface coating should have a Shore hardness of A80±10 degrees and an area of at least 0.3 m2.
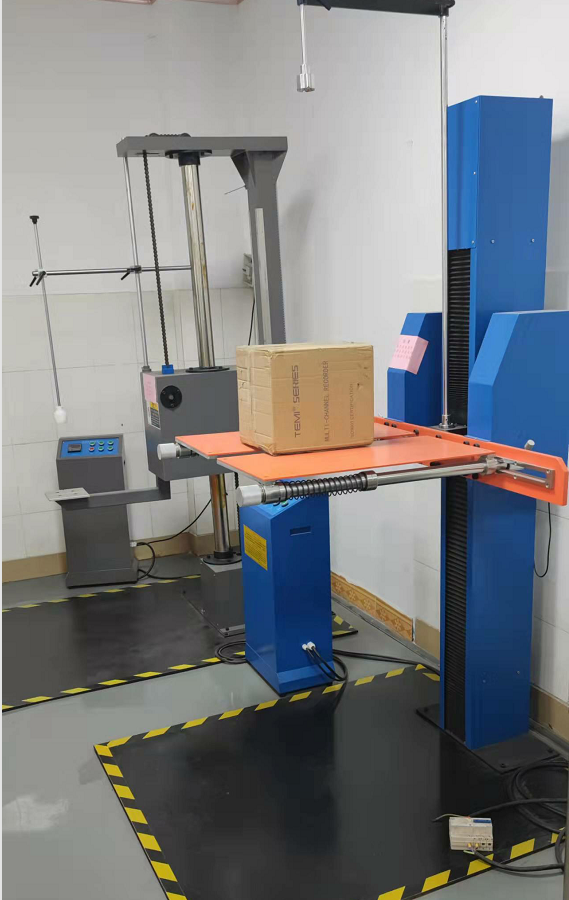
Image of Drop Testing Equipment:





 Weixin Service
Weixin Service

 DouYin
DouYin
 KuaiShou
KuaiShou











